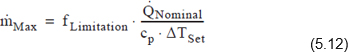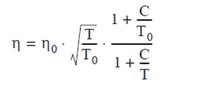Consumer Groups
In this dialog consumer groups can be defined.
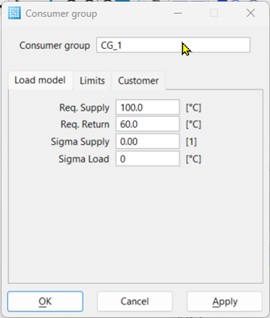
Load model Tab
- Supply and return target – Contains the target values for the supply and the return of the consumer group.
- Sigma Supply – Deviation of the return temperature when the load factor is changed.
- The return temperature is calculated according to the following formula:
- Sigma Load – Deviation from the return temperature when the flow temperature is modified. The return temperature is calculated according to the following formula.
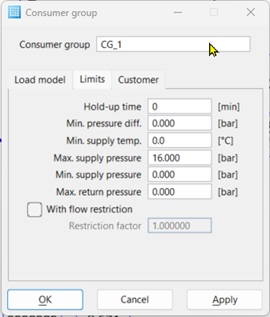
Limits Tab
- Retention time – Average retention time of the medium with a consumer in the case of design.
- Min. Difference of pressure – Minimum necessary customer pressure difference.
- Min. Supply temperature – Minimum necessary supply temperature.
- Max. Supply pressure – Maximum permissible customer supply pressure.
- Min. Supply pressure – Minimum supply pressure for all consumers belonging to the consumer group.
- Max. Return pressure – Maximum permissible pressure at the return of the consumer.
- With quantity delimitation – Activates the quantity delimitation of the associated consumers (only for the categories long-distance heating/long-distance cooling as well as in given rated outputs of the consumers). The maximum mass flow of a customer results from the rated output and the interpretation temperatures as well as the delimitation factor; see Gl. 5.12.
If no defaults are made, the consumers of this consumer group are calculated without quantity delimitation.
⚠Note that the defaults in the consumer group are possibly overwritten by individual settings on consumers. An explicit default of the maximum mass flow at the consumer has priority.
- Delimitation factor – Factor for the determination of the max. mass flow of a consumer in the network calculation. The maximum mass flow of a consumer effective in calculation is calculated as follows.
mMax is the maximum effective mass flow of a consumer in network calculation.
QNominal is the conclusion value of the consumer from the consumer data (individual network element).
ΔTSet is the target temperature difference of the consumer group for the case of design (the case in which the connected load is set).
f Limitation is the delimitation factor.
Customer Tab
Determines which consumption field is used for the transformation of a customer into a consumer when working with customer data. The transformation is described in the section Automatic production of consumers from customer data".
- Source – Marks the data field of the customer from which the target value is determined for the consumer. If source and target agree, a direct transfer of the value of the number takes place.
- Yearly hours – The field is activated, as soon as a quantity is selected under source. The appropriate flow size (heat flow, mass flow or volume flow) is then determined by division from the work/quantity and used for further conversions.
- Destination – The destination field in the generated consumer. Heat load, mass flow or through flow (depending upon medium) are available.
Medium Properties
- Medium – The name for the medium concerned.
- Standard density – The density of the medium in normal state.
- Calorific value – Optional information of the calorific value.
✍ With information of the calorific value, it is possible to give consumption values as connected loads (thermal outputs). The network calculation then takes over the conversion into mass flows using the calorific value.
- Dyn. Viscosity with standard conditions – The dynamic viscosity (not the kinematic viscosity!) of the medium.
- Sutherland constant – Constant for the conversion of the dynamic viscosity to another temperature than the standard temperature. The dynamic tenacity for a temperature T is calculated as follows:
- Pressure factor compressibility – Constant for the calculation of the gas compressibility subject to the pressure. The compressibility K is calculated with the pressure factor compressibility KPar as follows: